If you're here, chances are you're looking to get shredded and are wondering whether cutting carbs completely is the way to go. Well, before you start stocking up on cauliflower rice and zucchini noodles, let's take a closer look at the world of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates, the macronutrient everyone loves to hate, have been demonized for years. From the Atkins diet to the South Beach diet, we've been told that carbs are the enemy and must be eliminated to achieve our dream body. They have long been under scrutiny, polarizing the health-conscious community with contradicting opinions about their influence on achieving that shredded, sculpted physique.
But is that really the case?
Today, we're going to delve deep into the world of carbohydrates. We'll cover the different types of carbs, how they affect our body, and, most importantly, whether or not you should cut them completely to get shredded. So sit back, grab a bowl of oatmeal (yes, you can have carbs), and let's get started on this carb-tastic journey!
Related Article: Top 12 Lifestyle Hacks for a Shredded Physique
Understanding Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients (alongside proteins and fats) and are an essential energy source for our bodies. They can be found in various forms, such as sugars, starches, and fibres, and are present in numerous types of food, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products.
There are two primary types of carbohydrates: simple and complex. Let's dissect them one by one!
Simple Carbohydrates
Simple carbohydrates are molecules that consist of one or two sugar units. They are called simple sugars because they have a simple molecular structure, which makes them easy to break down and digest.
Some examples of simple sugars include glucose, fructose, lactose, and sucrose. These sugars are typically found in many foods, including fruits, honey, milk, and sugar. One of the critical characteristics of simple carbohydrates is that they are a quick energy source.
When you eat something that contains simple sugars, your body can quickly break down the sugars and convert them into glucose, which your cells use for fuel. This is why athletes often rely on simple carbohydrates before a race or game, as they provide a quick burst of energy that can help improve performance.
Complex Carbohydrates

Complex carbohydrates are a type of carbohydrate composed of long chains of sugar molecules. These chains usually comprise three or more sugar molecules linked together, which is why they are called "complex."
This molecular structure means that complex carbohydrates take longer to digest in the body than simple carbohydrates, which are made up of smaller molecules and quickly broken down into glucose.
You can find complex carbohydrates in different types of foods, including whole grains (such as brown rice and whole wheat bread), vegetables (such as broccoli and sweet potatoes), legumes (such as black beans and lentils), and nuts (such as almonds and walnuts). Few examples of complex carbohydrates include starch and dietary fiber.
How Are Carbohydrates Processed
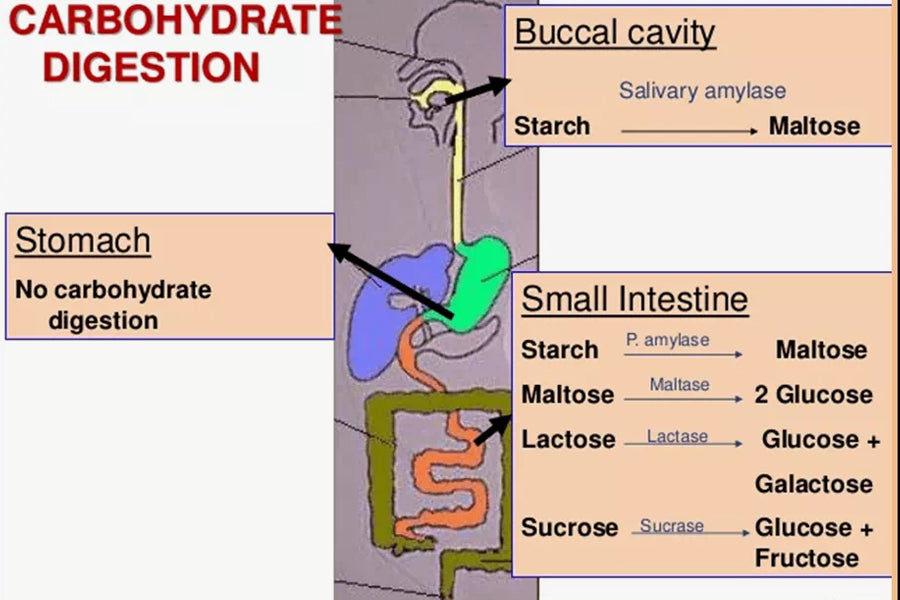
Carbohydrates are the fuel that keeps our bodies running like a well-oiled machine.
But how exactly does your body process them? Well, it all starts in the mouth, where saliva breaks down complex carbohydrates into smaller sugar molecules. From there, the carbohydrates travel down the esophagus and into the stomach, where they continue to be broken down by stomach acid.
The small intestine then takes over, releasing enzymes that entirely break down the carbohydrates into glucose, which is absorbed into the bloodstream and used for energy. So next time you indulge in a carb-heavy meal, remember all the hard work your body is doing behind the scenes to keep you up and running!
Some Carbs Are Better Than Others!
The fitness and nutrition industry has opposing opinions regarding carbohydrates. Some believe that carbohydrates lead to an increase in insulin levels, blood sugar, and body fat, ultimately causing harm to the body and health.
However, this extremist viewpoint is not shared by everyone. A group of individuals who possess knowledge of human physiology and the impact of carbohydrates on one's well-being and body image does not share this perspective.
In their opinion, it is essential to note that not all carbohydrates are created equal. Although all carbohydrates are eventually transformed into simple sugars like glucose and fructose, the primary energy source for our cells, the type and quantity of carbs ingested can influence one's health and fitness goals.
To claim that all carbohydrates simply turn into sugar is overly simplistic and fails to consider the intricacies of nutrition. The extent of processing food and the kind of food you consume can significantly impact insulin and blood sugar levels. For instance, eating a handful of pretzels will have a far different effect on blood sugar levels than eating a few servings of fruit.
The primary disparity between these two options is the presence of a fiber matrix. Unlike pretzels, fruits contain many essential vitamins, minerals, and water. Furthermore, processed foods have their fiber matric removed alongside most of the beneficial micronutrients naturally found in the food. Thus, it's advisable to include mostly whole, minimally processed foods in one's diet.
Of course, occasional processed food indulgences aren't necessarily harmful. They must, however, be viewed as temporary treats, not the everyday norm.
Fun Fact: You can incorporate Essential Amino Acids (EAAs) + Hydration in your diet for a punch of essential nutrients without fear of consuming too many carbs!
Now, let's get back to our main topic, whether to cut carbs completely to get shredded or not!
Should I Cut Carbs Completely to Get Shredded?

Contrary to what you may have read or heard, carbohydrates are not the only culprits responsible for the inability to lose weight or achieve a toned physique. Nor are they the reason behind a large portion of the population's overweight or obese individuals.
A study indicates that low-carb diets do not necessitate better weight loss outcomes than higher-carb, lower-fat diets. Further, cutting carbs from your diet can also lead to a decline in muscle preservation.
Besides this, there are several reasons why cutting carbs is unnecessary to achieve weight loss or a ripped physique, such as:
- Carbohydrates play an essential role in sparing protein, which curtails muscle protein breakdown.
- They also allow one to train more intensely, a crucial factor in high-intensity exercises such as HIIT and strength training, promoting muscle and strength building.
- Carbohydrates have been linked to boosting mood while reducing central fatigue.
- Also, carbohydrates can raise insulin levels, providing additional anti-catabolic benefits while lowering catabolic stress hormones such as cortisol.
It is also important to note that it is not easy for the body to store carbohydrates as body fat since it has to perform de novo lipogenesis (the process of creating fatty acids from carbohydrates in the body, which are then used for the production of different lipid molecules).
However, when one is dieting and in a calorie deficit, the body will prioritise using anything and everything available to maintain performance, functionality, and life. Hence, while low-carb diets can be effective, they are only sometimes more effective than a protein and calorie-matched higher-carb, lower-fat diet.
Moreover, low-carb diets may be necessary and beneficial in certain situations, including obesity, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle. Also, finding the perfect balance of consuming high-quality carbohydrates with other nutrients. Below are a few suggestions for finding that balance to get a shredded physique!
Finding the Right Balance
While eliminating carbs might seem like a shortcut to getting shredded, doing so is not the most sustainable or healthy option. The key is to strike a balance, focusing on consuming a moderate amount of high-quality carbohydrates that provide the necessary energy and nutrients without causing excessive weight gain.
Here are some tips for managing your carb intake to achieve that shredded look:
Choose Quality Carbs: Opt for whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes, which provide essential nutrients and energy without causing significant insulin spikes.
Time Your Carbs: Consume carbohydrates around your workouts when your body needs the energy most. This can help optimise your athletic performance and recovery.
Monitor Your Overall Intake: Keep track of your caloric intake, ensuring you maintain a caloric deficit to lose fat while providing enough fuel for your workouts. The Pre Workout Powder is the best way to fuel your workouts without adding calories to your body.
Listen to your body: Understand when you're experiencing legitimate hunger or just craving carbs. Fuel your body with quality carbohydrates when needed, and avoid unnecessary snacking.
Now, let's move to the best diet to get shredded. Yes, we know you still want to crack the code to achieve the killer physique you've been dreaming of!
The Perfect Diet to Lose Weight & Get Shredded

Well, both low-carb and high-carb diets can be effective for weight loss as long as the following requirements are met:
- Sufficient daily protein intake (0.8 grams per kg of body weight)
- Following a reduced-calorie diet
- Incorporating regular heavy weightlifting
- Doing cardio as needed to create and maintain a negative energy balance, although it is not mandatory for weight loss.
When it comes to choosing between a low-carb or high-carb diet, it's a matter of personal preference. Some people experience greater satiety and less hunger throughout the day while following a high-fat, low-carb diet.
On the other hand, some people feel sluggish and find it challenging to perform intense workouts due to low glycogen levels. A higher carb, lower fat diet may yield better weight loss results for such individuals.
Ultimately, the best diet for weight loss is highly individual. If you choose to retain carbohydrates in your diet, focus on consuming minimally processed and micronutrient-rich carbohydrates, such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits. Always remember to consult with your healthcare provider or nutritionist regarding your specific diet needs.
The occasional indulgence in refined carbohydrates is perfectly acceptable as long as it does not constitute most of your carbohydrate intake. It's worth noting that highly processed foods tend to contain more sugar and fat (i.e., more calories) and less fibre, reducing satiety and making it difficult to sustain a weight-loss diet.
Related Article: Carb Cycling for Weight Loss - A Step-by-Step Guide
The Verdict
Carbohydrates are essential macronutrients for the body, boosting energy levels, brain function, and overall bodily functions. Cutting carbs completely to get shredded is not the healthiest or the most effective approach. Eliminating them from your diet may help you lose weight quickly in the short term, but it is not sustainable or healthy in the long run.
Instead of completely cutting carbs, focus on incorporating healthy carbs into your diet by choosing whole, nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains. These foods are high in fibre, vitamins, and minerals and can support your weight loss goals healthily and sustainably.
Overall, it's important to remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach to nutrition and weight loss. It's best to consult a registered dietitian or healthcare professional about developing a personalised nutrition plan that works best for your unique needs and goals. So, go ahead and make carbs a part of your healthy and balanced diet!
Reading List
Article Sources
- Gardner, Christopher D., et al. "Effect of Low-Fat vs Low-Carbohydrate Diet on 12-Month Weight Loss in Overweight Adults and the Association With Genotype Pattern or Insulin Secretion: The DIETFITS Randomized Clinical Trial." JAMA, vol. 319, no. 7, Feb. 2018, pp. 667-79. Silverchair, https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.0245.
- Helms, Eric R., et al. "Evidence-Based Recommendations for Natural Bodybuilding Contest Preparation: Nutrition and Supplementation."Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, vol. 11, no. 1, May 2014, p. 20. BioMed Central, https://doi.org/10.1186/1550-2783-11-20.
- Song, Ziyi, et al. "Regulation and Metabolic Significance of De Novo Lipogenesis in Adipose Tissues." Nutrients, vol. 10, no. 10, Sept. 2018, p. 1383. PubMed Central, https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10101383.











